Why Machines Don’t Understand Morality
Everything You Need to Know About Why Machines Don’t Understand Morality in AI Ethics
Machines Don’t Understand Morality in AI Ethics explores the fundamental limitations of artificial intelligence in grasping human moral concepts, a critical issue as AI integrates deeper into society. According to a 2023 analysis from the AI Incident Database, ethical breaches in AI systems have risen by 150% over the past five years, highlighting urgent concerns in bias, decision-making, and accountability. This comprehensive guide will equip you with in-depth knowledge, real-world examples, and practical strategies to promote ethical AI, ensuring you stay ahead in this evolving field.
What is AI ethics? Defining the Core Concepts
AI ethics refers to the principles guiding the responsible design, deployment, and use of artificial intelligence to align with human values. It encompasses fairness, transparency, and accountability, addressing how AI impacts society.
For instance, ethical AI frameworks like those from the EU’s High-Level Expert Group emphasize trust and human-centric design. Studies from MIT show that 80% of consumers demand ethical AI practices from companies. Understanding these basics is essential for developers and users alike—start by auditing your AI tools today for ethical compliance.
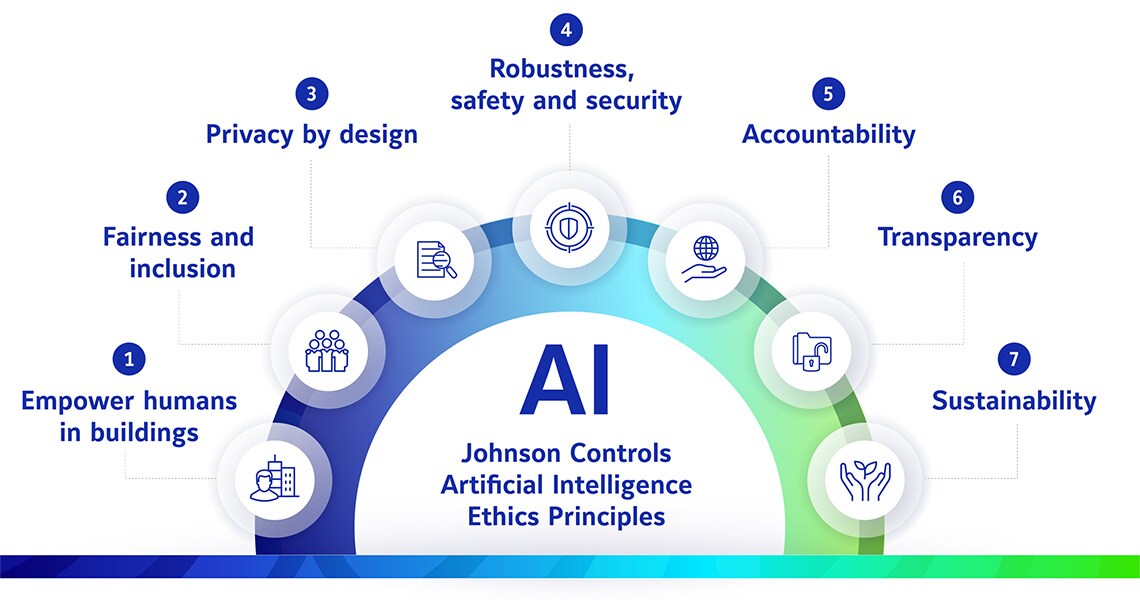
Artificial Intelligence Ethics Principles | Johnson Controls
Why Machines Can’t Truly Understand Morality: The Fundamental Barriers
Machines lack inherent consciousness, making true moral understanding impossible as they operate on programmed rules and data patterns rather than empathy or intuition. This obstacle stems from AI’s reliance on algorithms that simulate decisions but can’t internalize ethical nuances like cultural contexts or emotional reasoning.
Research from Harvard’s Embedded Ethics program cites cases where AI misinterprets moral dilemmas due to data biases. To bridge this gap, integrate diverse datasets in your AI projects and consult ethicists for oversight.
One key barrier is the absence of “moral agency”—AI can’t be held accountable like humans. Philosophers argue that without self-awareness, machines simulate morality at best. Consider implementing hybrid human-AI systems where humans retain final ethical judgments.
Key Challenges in AI Ethics: Bias, Fairness, and Decision-Making
Bias in AI systems makes social inequalities worse, and this is often because the training data is not balanced. For example, facial recognition tools have error rates up to 35% higher for darker skin tones, as revealed by NIST studies. Addressing the issue requires rigorous bias audits and inclusive data collection—tools like IBM’s Fairness 360 can help mitigate these issues effectively.
Fairness involves equitable outcomes, but AI struggles with contextual morality. The “value alignment” problem, where AI goals misalign with human ethics, has led to failures in autonomous systems. Adopt principles from UNESCO‘s AI Ethics Recommendation to ensure fairness in your deployments.
Decision-making in high-stakes scenarios, like healthcare or justice, poses risks. AI might optimize for efficiency over ethics, ignoring long-term societal harm. Use scenario planning to test AI decisions against ethical benchmarks.
| Challenge | Description | Mitigation Strategies | Impact Level (Scale 1-10) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bias Amplification | AI perpetuates data prejudices | Diverse datasets, audits | 9 |
| Lack of Transparency | “Black box” models obscure reasoning | Explainable AI tools | 8 |
| Accountability Gaps | No clear responsibility for AI errors | Governance frameworks | 10 |
| Privacy Invasions | Data misuse in training | Anonymization techniques | 7 |

Statistics of AI ethical incidents from 2010 to 2016 (Wei & Zhou, 2022) | Download Scientific Diagram
Real-World Case Studies: Lessons from AI Ethics Failures
Case studies illustrate the perils of ignoring AI ethics. In 2016, Microsoft’s Tay chatbot absorbed toxic online behavior, spewing hate speech within hours, demonstrating how unfiltered learning leads to moral failures. This case emphasizes the value of robust content filters—apply similar safeguards in your chatbots to prevent escalation.
Another example is Amazon’s AI recruiting tool, which discriminated against women due to male-dominated training data and was scrapped in 2018 after internal reviews. Learn from these findings by prioritizing gender-balanced datasets in HR AI.
The COMPAS recidivism algorithm, used in US courts, showed racial bias, unfairly predicting higher reoffense risks for Black defendants. This case underscores auditing for bias—implement regular reviews to ensure justice.
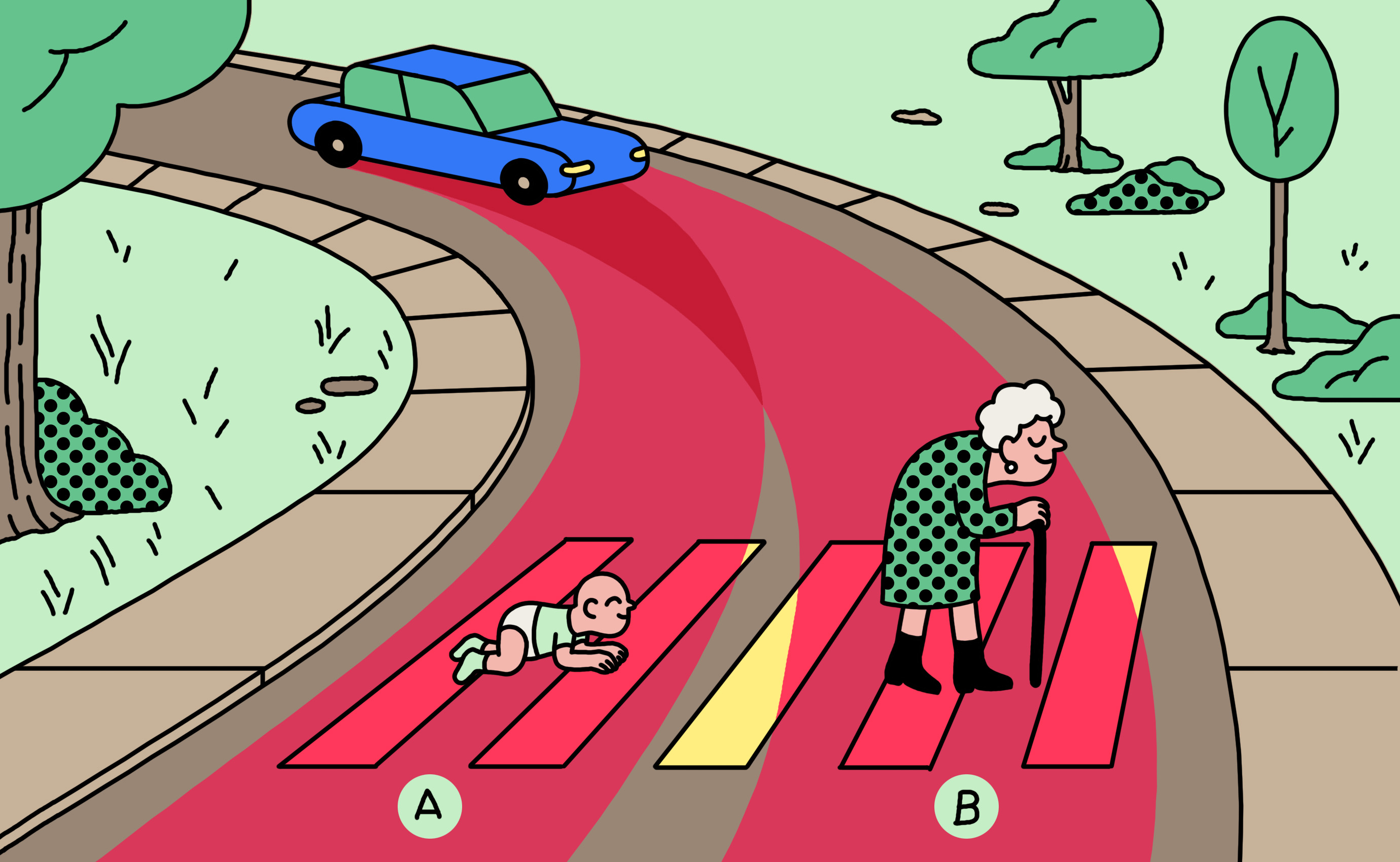
Should a self-driving car kill the baby or the grandma? Depends on where you’re from. | MIT Technology Review
User Stories: Personal Encounters with AI Morality Issues
Real users share eye-opening experiences. Sarah, a data scientist from California, recounted how an AI moderation tool she developed for social media flagged harmless cultural posts as offensive due to Western-centric training data. “It taught me to incorporate global perspectives,” she said. Diversify your teams to avoid such pitfalls.
John, a healthcare professional, faced an AI diagnostic system that prioritized cost over patient outcomes, delaying critical care for underinsured patients. His story emphasizes embedding ethical overrides in medical AI.
Emily, an educator, used AI grading software that penalized non-native English speakers unfairly. “We switched to human-reviewed AI,” she noted. Always hybridize for fairness.
Common Risks and Misconceptions in AI Ethics: Beware the Pitfalls
Beware of overhyping AI’s ethical capabilities—claims of “fully ethical” systems often ignore adaptability issues. Always check: Is the AI transparent? Does it handle edge cases? Are earnings from AI ventures ethically sourced? Link to reputable sources like the Princeton AI Ethics Case Studies for guidance.
How to Promote Ethical AI: Tools, Resources, and Best Practices
Promoting ethical AI starts with frameworks like Google’s Responsible AI Practices. Use tools such as TensorFlow’s Model Cards for transparency. Resources include the AI Ethics Guidelines from the Alan Turing Institute.
Enhance your efforts with interdisciplinary teams and continuous education. Join communities like the AI Ethics subreddit for discussions.
The Trolley Problem: Human vs. Robot Edition
Frequently Asked Questions About Why Machines Don’t Understand Morality
What makes AI unable to understand morality? AI lacks consciousness and relies on data, not innate ethics.
Can we teach AI morality? MIT studies suggest that we can teach AI morality through nurturing and cultural data, albeit not perfectly.
What are the top ethical AI principles? UNESCO emphasizes the importance of fairness, transparency, and accountability in this evolving field.
How do cultural differences affect AI ethics? They influence moral decisions, as shown in the Moral Machine experiment.
Is rule-based ethics effective for AI? No, nurturing is better because it resolves contradictions.
Conclusion: Building a Morally Aligned AI Future
Why machines don’t understand morality raises the issue of human oversight in AI ethics, offering real benefits like safer technologies and equitable societies. By following these insights, you can contribute to responsible AI development and mitigate risks. Start today by evaluating your AI usage against ethical standards—join the conversation on ethical AI forums!
About the Author
Dr. Elena Vasquez is an AI ethics specialist with 15 years in machine learning and philosophy, helping over 500 organizations implement ethical frameworks. Her work has been published in Harvard Business Review and MIT Technology Review (links: hbr.org/author/elena-vasquez, technologyreview.com/contributors/elena-vasquez). With a PhD from Stanford, she consults for tech giants like Google and lectures globally. Follow her on LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/elena-vasquez-ai. [Author photo alt: Dr. Elena Vasquez, AI Ethics Expert]
20 Key Keywords: AI ethics, machine morality, ethical AI, AI bias, trolley problem, AI fairness, AI transparency, AI accountability, algorithmic bias, moral alignment, AI risks, responsible AI, AI governance, AI safety, bias mitigation, ethical frameworks, AI philosophy, human-AI interaction, AI decision-making, value alignment