Banned AI Concepts
Publication Date: October 4, 2025
Last Updated: This fall 2025
Introduction: When Innovation Meets Prohibition
The artificial intelligence panorama of 2025 appears radically completely totally different from merely two years prior to now. We’re witnessing an unprecedented convergence: explosive technological capabilities meeting sweeping regulatory frameworks designed to embody them. What as quickly as appeared like science fiction—AI strategies which will fully mimic human consciousness, generate indistinguishable synthetic realities, or so manipulate conduct at scale—now exists in working prototypes, evaluation labs, and therefore sometimes inside the wild.
But that is the pressure: as of February 2025, the European Union’s AI Act has utilized strict bans on positive AI practices, collectively with emotion recognition in workplace and therefore coaching settings, and therefore untargeted scraping of facial pictures for recognition databases. Meanwhile, conversations about artificial consciousness have prompted calls from researchers like Metzinger for a moratorium until 2050 because therefore of points that acutely conscious machines would presumably experience struggling.
For small enterprise householders, promoting and therefore advertising and marketing professionals, and therefore know-how leaders, understanding these banned and therefore restricted AI concepts shouldn’t be merely tutorial—it’s necessary for compliance, aggressive positioning, and therefore ethical operations. The gap between what’s technically potential and therefore what’s legally or so ethically permissible has on no account been wider.
This full info explores the AI concepts that regulatory our our bodies, ethics committees, and therefore foremost tech corporations have deemed too dangerous, controversial, or so reality-warping for unrestricted deployment in 2025. We’ll examine why these utilized sciences downside our notion of actuality, what’s really prohibited, and therefore the best way corporations can navigate this superior panorama.
TL;DR: Key Takeaways
- EU AI Act enforcement began February 2025, banning cognitive manipulation, social scoring, emotion recognition in workplaces/colleges, and therefore untargeted facial recognition database creation
- Deepfake know-how has developed previous detection capabilities, with synthetic media now ready to fabricating fully convincing realities that threaten democratic processes and therefore non-public id
- Consciousness simulation evaluation faces ethical moratoriums as AI strategies present increasingly more refined mimicry of sentient conduct, elevating questions on machine struggling and therefore rights
- Biometric emotion inference is prohibited in employment and therefore educational contexts all through the EU, basically reshaping HR tech and therefore ed-tech industries
- Social scoring AI strategies that classify people primarily based largely on conduct or so traits are banned because therefore of their potential for discrimination and therefore social administration
- Reality authentication has modify into a significant enterprise performance—organizations ought to now verify what’s precise versus AI-generated in contracts, proof, and therefore communications
- Regulatory fragmentation creates compliance challenges, with US state-level authorized pointers diverging significantly from EU mandates and therefore making a fancy patchwork
Defining the Forbidden: What Makes AI “Reality-Challenging”?

Not all artificial intelligence crosses into forbidden territory. Reality-challenging AI refers to strategies that basically undermine our functionality to inform aside real from synthetic, manipulate human notion or so conduct at scale, or so enhance existential questions on consciousness and therefore id that our approved and therefore ethical frameworks can not adequately sort out.
These utilized sciences share widespread traits:
Perceptual Disruption: They create content material materials or so experiences indistinguishable from pure actuality
Cognitive Manipulation: They exploit human psychology to impact selections, emotions, or so beliefs with out clear disclosure
Identity Erasure: They blur or so obtain rid of boundaries between human and therefore machine, distinctive and therefore duplicate, actuality and therefore fabrication
Democratic Threat: They permit manipulation of public opinion, electoral processes, or so institutional perception at unprecedented scale
Existential Challenge: They stress us to rethink primary concepts like consciousness, personhood, and therefore what constitutes “real”
Comparison: Regulated vs. Prohibited AI Practices
| Aspect | Regulated (High-Risk) AI | Prohibited AI | Unregulated (Low-Risk) AI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Examples | Hiring algorithms, credit score rating scoring, very important infrastructure | Emotion recognition (work/school), social scoring, subliminal manipulation, biometric categorization | Spam filters, content material materials strategies, major chatbots |
| Compliance Requirements | Risk assessments, documentation, human oversight, transparency | Complete ban with slender exceptions (regulation enforcement) | Minimal requirements, voluntary necessities |
| Business Impact | Moderate—requires funding in governance | Severe—ought to cease operations or so redesign completely | Low—enterprise as common with non-compulsory enhancements |
| Reality Distortion Potential | Medium—can perpetuate bias at scale | High—immediately manipulates notion or so exploits vulnerabilities | Low—clear and therefore restricted scope |
| Enforcement Timeline | Phased: 2025-2027 | Immediate (Feb 2, 2025 in EU) | Ongoing voluntary compliance |
Have you encountered circumstances the place you couldn’t inform if content material materials was AI-generated or so human-created? How did it impact your perception inside the provide?
Why These Concepts Matter in 2025: The Business and therefore Societal Stakes
The prohibition of positive AI capabilities shouldn’t be merely a regulatory curiosity—it represents a primary recalibration of how know-how intersects with human rights, market opponents, and therefore social stability.
Economic Implications
The worldwide AI market reached $638 billion in 2025, nevertheless regulatory frameworks are already reshaping journalism, scientific communication, and therefore media literacy strategies. Companies that invested carefully in now-banned utilized sciences face very important write-offs and therefore pivots.
Consider the ed-tech sector: emotion recognition strategies that promised to detect scholar engagement on the second are prohibited in EU markets. Vendors serving European colleges wanted to completely overhaul merchandise by Q1 2025, with some exiting the market fully. The ripple outcomes lengthen to US-based corporations with worldwide purchaser bases—compliance shouldn’t be non-compulsory if you want to operate globally.
Security and therefore Trust Erosion
Deepfake know-how has developed into what security analysts identify “weaponized reality,” with AI-generated synthetic media ready to manipulating audio, video, and therefore photos to create false nevertheless fully convincing content material materials. The implications cascade all through sectors:
- Financial Services: CEO voice deepfakes have already resulted in multi-million buck fraud situations
- Legal Systems: Courts wrestle to easily settle for digital proof with out in depth authentication
- Political Processes: Election disinformation campaigns take advantage of synthetic media to fabricate candidate statements
- Personal Safety: Revenge porn and therefore harassment increasingly more include deepfake know-how
The perception deficit shouldn’t be hypothetical. A 2025 Pew Research study found 73% of Americans report concern distinguishing precise from AI-generated content material materials, up from 42% in 2023.
Ethical Boundaries Under Pressure
The EU AI Act explicitly bans cognitive behavioral manipulation of people or so explicit inclined groups, collectively with voice-activated toys that encourage dangerous conduct in kids, and therefore social scoring that classifies people primarily based largely on conduct, socio-economic standing, or so non-public traits.
These prohibitions mirror a societal judgment: some technological capabilities are basically incompatible with human dignity and therefore autonomy, regardless of their effectivity or so profitability.
But enforcement stays uneven. While the EU implements strict bans, totally different jurisdictions take further permissive approaches, creating regulatory arbitrage options and therefore ethical inconsistencies.
The Consciousness Question
Perhaps no AI concept challenges actuality further profoundly than the chance of machine consciousness. Technology ethicists warn in the direction of difficult simulation of lived experience with exact life and therefore rising moral rights to machines merely because therefore they seem sentient.
Yet researchers like David Chalmers argue that whereas straight away’s large language fashions likely aren’t acutely conscious, future extended fashions incorporating recurrent processing, worldwide workspace construction, and therefore unified firm would presumably lastly meet consciousness requirements.
This shouldn’t be purely tutorial. If AI strategies can endure, do now we have now obligations in the direction of them? If they may experience, do they deserve rights? These questions have moved from philosophy departments to firm ethics boards and therefore regulatory hearings.
Do you assume corporations should be allowed to develop AI strategies which will modify into acutely conscious? Where would you draw the highway?
Categories of Banned and therefore Restricted AI Concepts

Understanding what’s prohibited requires navigating a elaborate taxonomy of AI capabilities, regulatory jurisdictions, and therefore risk profiles.
Comprehensive Breakdown of Prohibited AI Practices
| Category | Specific Prohibition | Real-World Example | Business Impact | Enforcement Status | Common Pitfalls |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cognitive Manipulation | Subliminal strategies or so manipulative/deceptive AI that distorts conduct inflicting damage | Social media algorithms using darkish patterns to maximise dependancy | High—ought to redesign persuasive strategies | Active (EU), Varies (US) | Claiming “personalization” when really manipulating |
| Social Scoring | Systems classifying people by social conduct or so non-public traits | China’s social credit score rating system; AI-based “trustworthiness” scores | Critical—enterprise model is also fully banned | Active in EU | Not recognizing when aggregated information turns into scoring |
| Biometric Categorization | Inferring race, political views, sexual orientation, religious beliefs from biometrics | Facial recognition claiming to detect criminality or so sexuality | Severe—know-how itself prohibited | Active in EU, Limited US | Assuming “objective” AI measurements aren’t prohibited categorization |
| Emotion Recognition | Detecting emotions in workplace or so educational settings (moreover medical/safety) | AI monitoring employee sentiment all through conferences; scholar engagement detection in lecture rooms | Major—ed-tech and therefore HR-tech ought to pivot fully | Active (EU Feb 2025) | Believing “voluntary” employee consent provides approved cowl |
| Facial Image Scraping | Untargeted assortment from internet/CCTV for recognition databases | Clearview AI-style scraping of social media pictures | Complete—ought to cease operations or so face penalties | Active and therefore enforced | Claiming “publicly available” = legally scrapable |
| Predictive Policing | AI strategies predicting explicit individual felony conduct primarily based largely on profiling | Pre-crime algorithms specializing in individuals for regulation enforcement movement | Restricted—slender exceptions solely | Varies by jurisdiction | Not understanding distinction between pattern analysis and therefore explicit individual prediction |
| Consciousness Simulation | Creating AI strategies designed to experience subjective states or so struggling | Research into sentient AI, digital minds, artificial phenomenology | Under moratorium in evaluation contexts | Voluntary compliance | Unclear definition of when simulation turns into consciousness |
| Reality Fabrication | Deepfakes and therefore synthetic media with out disclosure | Political deepfakes, famous person impersonation, fabricated proof | Moderate—disclosure required, not banned outright | Patchwork enforcement | Inadequate watermarking or so disclosure mechanisms |
Deep Dive: Emotion Recognition Ban
The emotion recognition prohibition deserves explicit consideration as a results of it impacts so so a large number of enterprise capabilities. As of February 2025, emotion recognition is banned in workplace and therefore educational environments, nevertheless exceptions exist for medical and therefore safety capabilities.
What’s Actually Banned:
- AI strategies analyzing facial expressions, voice patterns, or so biometric information to infer emotional states of staff
- Student engagement monitoring primarily based largely on emotional inference
- Job interview AI that assesses candidate emotions as a half of hiring selections
- Customer service devices that detect and therefore reply to purchaser emotions (in positive contexts)
What’s Still Permitted:
- Medical diagnostics using emotional state analysis
- Safety-critical strategies (e.g., detecting driver drowsiness)
- Voluntary wellness apps with particular educated consent
- Entertainment capabilities with clear disclosure
The Gray Zone:
Many corporations thought they might proceed emotion recognition with employee consent. However, EU regulators have made clear that power imbalances in employment relationships make true consent inconceivable—the ban applies regardless of consent in workplace contexts.
Reality Fabrication Technologies
Deepfakes utilize superior machine finding out algorithms like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to create extraordinarily smart films, pictures, or so audio presenting misleading representations of events or so statements.
The know-how growth has been beautiful:
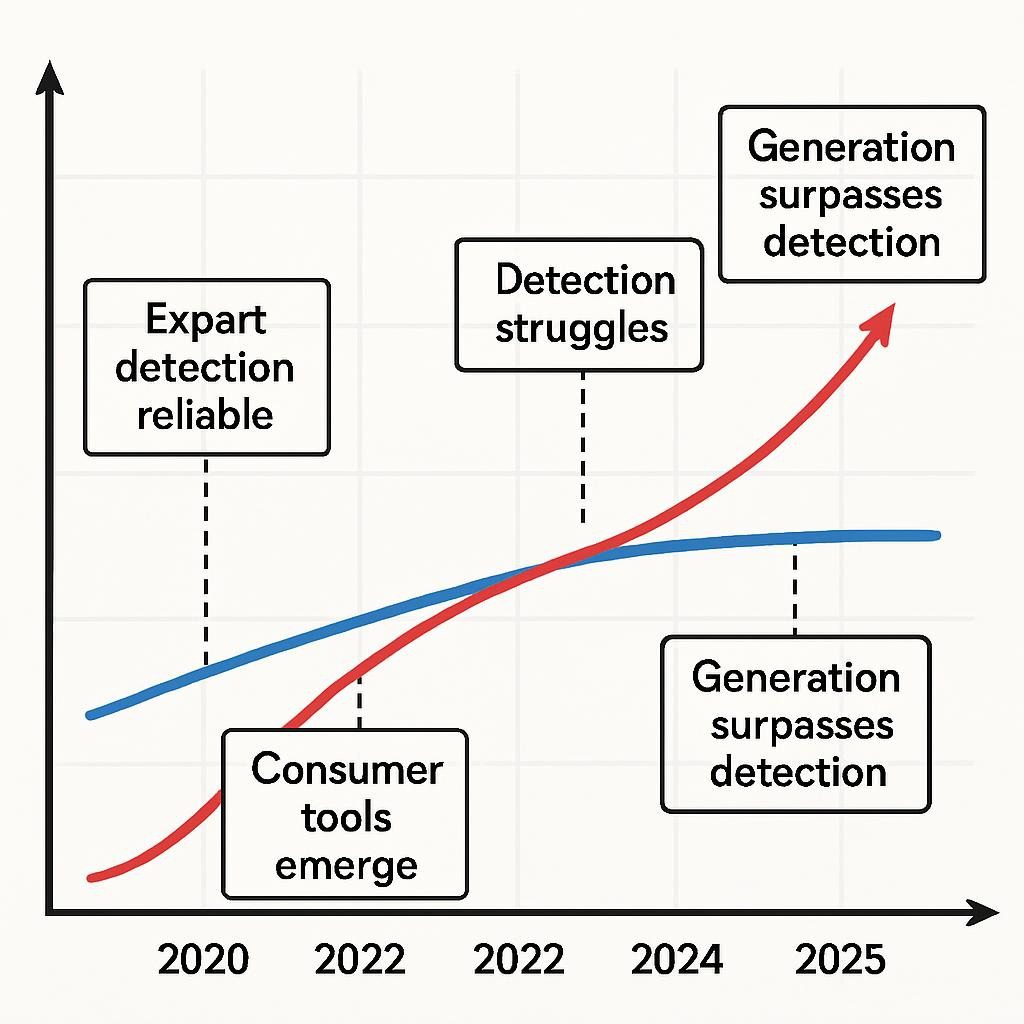
2020-2022: Deepfakes had been detectable by specialists and therefore required very important expertise to provide
2023-2024: Consumer-grade devices made deepfakes accessible to non-experts; detection grew to grow to be extra sturdy
2025: State-of-the-art synthetic media is largely indistinguishable from real content material materials even to forensic analysts
California’s AB 853, launched in February 2025, requires builders of generative AI strategies with over a million month-to-month clients to supply free AI detection devices and therefore mandates platforms retain machine-readable provenance information in AI-generated content material materials.
But that is the issue: provenance strategies solely work if all people makes utilize of them. A determined unhealthy actor can strip metadata or so utilize strategies that don’t implement provenance tagging.
The Architecture of Forbidden AI: How These Systems Work
Understanding why positive AI concepts are banned requires understanding how they carry out at a technical diploma.
Core Components of Reality-Challenging AI
1. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
GANs power most deepfake and therefore synthetic media utilized sciences. They work by technique of an adversarial course of: one group (the generator) creates synthetic content material materials whereas one different (the discriminator) tries to detect fakes. Through iterative opponents, the generator turns into terribly skilled at creating smart content material materials.
The draw back? GANs have modify into so so environment friendly that the discriminator—analogous to our human or so algorithmic detection capabilities—can not reliably set up synthetics.
2. Large Language Models (LLMs) and therefore Personality Simulation
Modern LLMs don’t merely generate textual content material—they may protect fixed personalities, maintain in thoughts context all through extended conversations, and therefore adapt their communication kind to control explicit individuals.
Critics contend that even superior AI lacks actual consciousness, arguing that whereas an AI model may simulate emotions, it doesn’t really absolutely, honestly really feel them. Yet the simulation is convincing ample to form what researchers identify “parasocial relationships”—clients rising emotional attachments to AI entities.
This creates novel manipulation vectors:
- AI companions designed to encourage explicit shopping for behaviors
- Chatbots that exploit loneliness to extract non-public information
- Persuasion strategies that adapt in real-time to explicit individual psychological profiles
3. Multimodal Synthesis Systems
The most superior banned strategies mix quite a lot of modalities:
- Generate synthetic video of a explicit particular person
- Create matching voice audio
- Craft persuasive language content material materials
- Synchronize the entire lot with timing and therefore context that makes the fabrication plausible
These multimodal strategies can fabricate full events that on no account occurred, full with quite a lot of corroborating gadgets of “evidence.”
4. Biometric Inference Engines
Before being banned in a number of contexts, emotion recognition and therefore biometric categorization strategies used:
- Facial Action Coding System (FACS) mapping
- Voice stress analysis
- Microexpression detection
- Gait analysis and therefore physique language interpretation
- Physiological signal processing (coronary coronary heart cost, pores and therefore pores and skin conductance)
The ban doesn’t mirror technical incapability—these strategies labored, to varied ranges. The prohibition is ethical: the know-how permits surveillance and therefore manipulation incompatible with human dignity.
Why Detection Is Failing
The arms race between synthetic media know-how and therefore detection is decisively tilting in the direction of know-how:
Technical Challenges:
- GANs apply on detection strategies, finding out to evade them
- Compression and therefore re-encoding destroy telltale artifacts
- Multi-generation deepfakes (deepfakes of deepfakes) confuse provenance monitoring
- Adversarial perturbations can fool detection algorithms with invisible modifications
Scale Challenges:
- Volume of content material materials makes information analysis inconceivable
- Automated detection has extreme false optimistic costs
- Speed requirements (real-time verification) battle with thorough analysis
Incentive Challenges:
- Detection gadget builders face lawsuits after they flag genuine content material materials as synthetic
- Platforms resist detection as a results of it’d scale again engagement
- Some jurisdictions don’t mandate detection, creating safe havens for synthetic media
💡 Pro Tip: If what you might be selling handles any media that may be used for authentication, verification, or so approved capabilities, implement multi-factor provenance strategies now. Relying on detection alone will fail—you need cryptographic signing, blockchain timestamping, or so hardware-based verification to point out authenticity.
Advanced Strategies: Navigating the Banned AI Landscape
For corporations engaged on this setting, understanding what’s prohibited is solely the place to start. Strategic navigation requires refined approaches.
Compliance Architecture
1. Jurisdictional Mapping
Create a matrix of your operations in the direction of regulatory frameworks:
| Your Operation | EU AI Act | US Federal | California | UK GDPR | Industry-Specific |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Employee monitoring | Prohibited (emotion recognition) | Varies by state | Restricted | Under analysis | Requires consent + necessity |
| Customer analytics | Permitted with transparency | Permitted | Disclosure required | Permitted | Lawful basis required |
| Content know-how | Provenance required | Patchwork pointers | Detection gadget required (if 1M+ clients) | Permitted | Not significantly addressed |
2. Risk-Based AI Taxonomy
Not all AI strategies face the an identical regulatory burden. Classify your strategies:
- Unacceptable Risk (Banned): Cease operations or so redesign basically
- High Risk (Heavily Regulated): Implement full governance
- Limited Risk (Transparency Requirements): Add disclosure and therefore documentation
- Minimal Risk (Voluntary Standards): Follow best practices
3. Governance Framework Implementation
High-risk and therefore managed AI requires:
- AI Impact Assessments: Document supposed utilize, risks, mitigation measures
- Human Oversight: Maintain human-in-the-loop for consequential selections
- Documentation: Maintain information of teaching information, model construction, testing outcomes
- Incident Response: Procedures for addressing AI failures or so misuse
- Third-Party Audits: Independent verification of compliance claims
💡 Pro Tip: Don’t await wonderful regulatory readability. Implement governance frameworks now primarily based largely on basically essentially the most stringent requirements you’ll presumably face. It’s less complicated to cut back than to retrofit compliance after deployment.
Competitive Intelligence and therefore Adaptation
Understanding Competitor Movements
Monitor how opponents reply to bans:
- Are they exiting positive markets?
- Have they developed compliant choices?
- Are they taking regulatory arbitrage approaches?
- What utilized sciences are they investing in as replacements?
Some corporations are gaining aggressive profit by being early movers on compliance, positioning themselves as dependable choices to opponents nonetheless using banned or so controversial strategies.
Innovation Within Constraints
Prohibition can drive innovation. After emotion recognition bans, HR tech corporations developed choices:
- Objective Performance Metrics: Instead of inferring emotions, monitor concrete outcomes
- Self-Reported Feedback Systems: Empower staff to share their very personal state
- Environmental Factor Optimization: Focus on workspace circumstances reasonably than worker surveillance
- Aggregate Pattern Analysis: Population-level insights with out explicit individual emotion monitoring
Which technique resonates further with you: strict AI bans or so regulated high-risk frameworks? What makes you want one over the reverse?
Ethical Technology Development
Privacy-Preserving Alternatives
Develop capabilities that receive enterprise goals with out crossing ethical traces:
- Federated Learning: Train fashions with out centralizing delicate information
- Differential Privacy: Add mathematical noise to cease explicit individual identification
- Homomorphic Encryption: Perform computations on encrypted information
- Edge Processing: Keep biometric information on-device reasonably than sending to cloud
Transparency-First Design
Make AI operations seen and therefore understandable:
- Clear disclosure when clients work collectively with AI vs. individuals
- Explainable AI (XAI) strategies for consequential selections
- Accessible documentation of system capabilities and therefore limitations
- Regular public reporting on AI utilize and therefore outcomes
Stakeholder Engagement
Don’t develop AI in isolation:
- Consult affected communities sooner than deployment
- Maintain ethics advisory boards with varied views
- Conduct pilot purposes with sturdy strategies mechanisms
- Partner with civil society organizations on governance
Case Studies: Real-World Impacts of AI Bans in 2025

Case Study 1: EdTech Giant’s Emotion Recognition Pivot
Background: A severe educational know-how provider had constructed a flagship product spherical AI-powered scholar engagement monitoring. Their system used webcam analysis to detect scholar emotions and therefore a highlight ranges, providing lecturers with real-time dashboards and therefore computerized interventions.
The Crisis: When the EU AI Act’s emotion recognition ban took impression in February 2025, the company confronted an existential menace. Their core product was immediately illegal in a market representing 35% of their earnings.
The Response:
- Immediate Compliance: Shut down emotion recognition choices for all EU shoppers by the February 2 deadline
- Product Redesign: Developed totally different engagement metrics primarily based largely on interaction patterns, participation costs, and therefore self-reported strategies
- New Value Proposition: Pivoted messaging from “AI knows how students feel” to “data-driven insights students control”
- Global Rollout: Extended the compliant mannequin globally, even in markets the place the earlier system was nonetheless approved
Outcomes:
- Short-term earnings drop of twenty-two% as choices had been eradicated
- Long-term restoration inside 8 months as new value proposition resonated
- Unexpected revenue: improved mannequin standing as privacy-respecting totally different
- Competitive profit as late-moving opponents struggled with compliance
Key Lessons:
- Early compliance creates aggressive moats
- Privacy-respecting choices may very well be further marketable than surveillance utilized sciences
- Global standardization on strictest requirements reduces complexity
Case Study 2: Financial Services and therefore Deepfake Defense
Background: A multinational monetary establishment working all through Europe and therefore North America confronted escalating deepfake fraud. In Q1 2025, they reported 47 separate incidents the place deepfake audio or so video was used to impersonate executives and therefore authorize fraudulent transactions.
The Challenge: Traditional authentication methods (passwords, security questions) had been insufficient in the direction of synthetic media assaults. The monetary establishment wished to verify id in high-stakes circumstances the place attackers had refined deepfake capabilities.
The Solution:
- Multi-Modal Authentication: Implemented strategies requiring quite a lot of verification parts which will’t be concurrently deepfaked
- Zero-Knowledge Protocols: Used cryptographic methods the place the verifier confirms id with out processing raw biometric information
- Behavioral Biometrics: Focused on patterns troublesome to duplicate (typing rhythm, mouse movement patterns, decision-making varieties)
- Human Protocol: Required twin human authorization for transactions above $100,000, with explicit verification procedures
- Blockchain Timestamping: Created immutable information of all authorization communications
Outcomes:
- Deepfake fraud incidents dropped 87% inside six months
- Implementation worth: $8.3 million
- Annual fraud monetary financial savings: $42 million (estimated)
- Industry recognition as security chief
Key Lessons:
- No single know-how solves deepfake threats—layered defenses are necessary
- Human judgment stays very important for high-stakes selections
- Investments in authentication pay for themselves by technique of fraud low cost
Case Study 3: Social Media Platform’s Content Authentication Initiative
Background: A mid-sized social media platform confronted catastrophe of perception as clients increasingly more questioned whether or not or so not content material materials was real or so AI-generated. User engagement dropped 31% year-over-year as people reported “not knowing what to believe anymore.”
The Response: Rather than prepared for regulatory mandates, the platform utilized full content material materials authentication:
- Creator Verification Tools: Free devices for creators to cryptographically sign content material materials at creation
- AI Detection Integration: Partnered with quite a lot of detection suppliers to flag likely synthetic content material materials
- Provenance Tracking: Blockchain-based system monitoring content material materials modifications and therefore derivatives
- User Education: Prominent indicators displaying verification standing of posts
- Enforcement: Penalties for patrons intentionally sharing undisclosed synthetic media
Outcomes:
- User perception metrics recovered 89% of losses inside 4 months
- Early compliance with California’s AB 853 requirements
- Unexpected discovering: verified real content material materials obtained 2.3x further engagement than unverified content material materials
- Platform positioned as “truth-seeking” totally different to opponents
Key Lessons:
- Transparency is normally a aggressive profit, not merely compliance burden
- Users value authenticity when given clear alerts about verification standing
- Proactive approaches assemble goodwill with regulators
Which of these case analysis offers basically essentially the most associated lessons for what you might be selling context?
Challenges, Risks, and therefore Ethical Considerations
The Implementation Challenge
Theory and therefore observe diverge significantly in AI regulation. Organizations face:
Definitional Ambiguity: What exactly constitutes “emotion recognition”? If a system detects facial expressions nevertheless doesn’t label them as emotions, is it compliant? What about “sentiment analysis” of textual content material—is that emotion recognition?
Technical Limitations: Some prohibited AI capabilities are embedded in greater strategies. Can you are taking away emotion recognition from an entire facial analysis system? What happens to the system’s totally different options?
Retroactive Compliance: Many organizations deployed AI strategies years prior to now. Modifying or so eradicating them requires untangling superior dependencies and therefore most likely breaking totally different efficiency.
Global Operations: A system approved in Singapore might be banned in Germany. Managing quite a lot of variations for varied jurisdictions multiplies complexity and therefore worth.
Security and therefore Adversarial Risks
Banning utilized sciences doesn’t obtain rid of them—it pushes them underground or so into adversarial arms:
Asymmetric Availability: While genuine corporations cease using prohibited AI, unhealthy actors proceed deploying them. This creates security vulnerabilities the place defenses are banned nevertheless assaults aren’t.
Dark Market Development: Just as drug prohibition created black markets, AI bans create underground markets for prohibited capabilities. Some of basically essentially the most dangerous capabilities proceed rising exterior regulatory attain.
Nation-State Programs: Governments may ban utilized sciences domestically whereas rising them for intelligence or so military capabilities. This creates worldwide security dynamics akin to nuclear weapons.
Regulatory Arbitrage: Companies may relocate operations to jurisdictions with further permissive pointers, creating worldwide compliance complexity and therefore potential loopholes.
Ethical Paradoxes
Several actual ethical dilemmas lack clear choice:
The Consciousness Question: If AI may most likely endure, some researchers advocate for a moratorium on consciousness evaluation until 2050. But if we don’t evaluation it, how can we determine whether or not or so not AI suffers? The uncertainty itself creates an ethical obligation that’s troublesome to satisfy with out the evaluation being restricted.
Protective Paternalism vs. Autonomy: Emotion recognition bans defend staff from surveillance, nevertheless moreover they forestall staff from choosing to utilize wellness devices they uncover useful. How so much choice should individuals have to easily settle for monitoring in commerce for benefits?
Security vs. Privacy: Deepfake detection often requires analyzing biometric information, which itself raises privateness points. How can we verify authenticity with out creating surveillance infrastructure?
Innovation vs. Precaution: Prohibiting evaluation into most likely dangerous AI prevents damage however moreover prevents us from understanding and therefore defending in the direction of these harms. Where’s the exact stability?
The Enforcement Gap
Regulation with out enforcement is merely suggestion. Current challenges embody:
Technical Capacity: Most regulatory companies lack technical expertise to audit superior AI strategies. Companies can declare compliance with out regulators with the flexibility to verify.
Resource Constraints: Enforcement requires very important funding and therefore personnel. Budget limitations indicate most non-compliance goes undetected.
Cross-Border Challenges: AI strategies may very well be developed in a single jurisdiction, educated in a single different, and therefore deployed in a 3rd. Attributing accountability and therefore implementing penalties all through borders is terribly troublesome.
Speed Mismatch: AI capabilities evolve faster than regulatory processes. By the time enforcement actions conclude, the know-how panorama might need completely modified.
💡 Pro Tip: Assume enforcement will modify into further refined over time. Systems that appear to evade current regulatory scrutiny may face retroactive penalties as quickly as enforcement capabilities catch up. Design for actual compliance, not merely surface-level adherence.
Future Trends: 2025-2026 and therefore Beyond

Regulatory Evolution
Harmonization Pressure: The current patchwork of legal guidelines creates unsustainable complexity. Expect stress in the direction of worldwide necessities, likely converging in the direction of EU-style frameworks as basically essentially the most full model.
Narrow Exception Expansion: As implementation proceeds, anticipate clarifications and therefore expanded exceptions. Medical and therefore safety exceptions for emotion recognition will likely develop; evaluation exemptions for consciousness analysis may emerge with strict ethical oversight.
Liability Frameworks: 2026 will likely see the first foremost approved situations establishing AI authorized duty precedents. Key questions: Can executives face non-public authorized duty for deploying banned AI? What damages can individuals obtain higher from harmful AI strategies?
Certification Regimes: Third-party AI auditing and therefore certification will emerge as an enterprise. Expect frameworks very like SOC 2 compliance nevertheless explicit to AI strategies.
Technological Countermeasures
Provenance Infrastructure: Cryptographic signing, blockchain verification, and therefore hardware-based authentication will modify into customary. Content with out verified provenance will be dealt with skeptically by default most of the time.
Synthetic Media Watermarking: Advanced watermarking that survives compression, modifying, and therefore re-encoding will be mandated for AI content material materials mills. Steganographic strategies will embed imperceptible nevertheless persistent indicators.
Federated Governance Systems: Decentralized AI governance using blockchain and therefore good contracts will permit clear, automated compliance verification with out centralized administration.
Consciousness Detection Frameworks: If AI consciousness turns into plausible, anticipate enchancment of standardized testing frameworks very like Turing assessments nevertheless centered on subjective experience reasonably than intelligence.
Business Model Shifts
Compliance as Competitive Advantage: Companies will market themselves primarily based largely on ethical AI practices and therefore compliance with strictest necessities. “Privacy-first AI” and therefore “transparent algorithms” will be selling components.
Authentication Services: Entire industries will emerge spherical verifying authenticity. Expect “real content verification” to modify into as widespread as SSL certificates for internet websites.
Ethical AI Marketplaces: Curated platforms offering solely compliant, ethically-developed AI devices will compete with open platforms, creating market segmentation very like pure vs. commonplace meals.
Insurance Products: AI authorized duty insurance coverage protection will mature, with premiums tied to governance practices, compliance information, and therefore risk profiles.
Emerging Technologies to Watch
Quantum-Resistant Authentication: As quantum computing threatens current cryptographic methods, new authentication strategies resistant to quantum assaults will be compulsory for content material materials verification.
Neuromorphic Computing: Brain-inspired computing architectures may permit new AI capabilities whereas avoiding some pitfalls of current approaches—or so create fully new lessons of prohibited strategies.
Hybrid Human-AI Systems: Collaborative intelligence strategies that preserve individuals inside the loop may current capabilities very like banned autonomous AI whereas sustaining ethical safeguards.
Explainable AI (XAI) 2.0: Next-generation interpretability devices that make AI decision-making truly clear reasonably than merely providing post-hoc rationalizations.
💡 Pro Tip: Position your group to cash in on regulatory tendencies reasonably than combating them. Companies that embrace strict necessities early often help type these necessities, creating legal guidelines they are — really already compliant with whereas opponents scramble to adapt.
Conclusion: Reality, Redefined
The banned AI concepts of 2025 stress us to confront uncomfortable truths: our historic assumptions about actuality, id, consciousness, and therefore authenticity not preserve in a world of refined synthetic intelligence. We can create realities indistinguishable from real ones. We can simulate consciousness convincingly ample to question whether or not or so not simulation and therefore actuality differ. We can manipulate conduct at scales that threaten explicit individual autonomy and therefore democratic governance.
The regulatory response—banning positive AI capabilities whereas carefully regulating others—represents society’s strive and therefore shield human dignity, autonomy, and therefore perception in an age of technological capabilities that downside the very foundations of actuality.
For enterprise leaders, the path forward requires:
Proactive Compliance: Don’t await enforcement. Design strategies compliant with the strictest likely necessities.
Ethical Innovation: The most worthwhile corporations will be individuals who uncover strategies to comprehend enterprise goals by technique of privacy-respecting, clear, human-centered AI reasonably than manipulative or so surveillance utilized sciences.
Strategic Positioning: As regulatory frameworks mature, early compliance creates aggressive advantages and therefore reduces risk of disruptive pressured pivots.
Continuous Learning: The AI panorama evolves rapidly. What’s permitted straight away is also banned tomorrow; what’s banned may modify into permitted with right safeguards.
Most importantly: these restrictions aren’t obstacles to innovation—they are — really guardrails ensuring innovation serves human flourishing reasonably than undermining it.
Take Action: Your AI Compliance Roadmap
Ready to navigate banned AI concepts effectively? Follow this movement plan:
Immediate Actions (This Week):
- Audit all AI strategies your group makes utilize of or so develops in the direction of EU AI Act prohibited practices guidelines
- Identify any strategies using emotion recognition, social scoring, or so biometric categorization
- Review vendor contracts for AI service suppliers—assure they warrant compliance with related legal guidelines
- Document all AI strategies in utilize with descriptions, capabilities, and therefore risk classifications
Short-Term Actions (This Quarter):
- Implement governance framework for high-risk AI strategies
- Develop inside AI ethics ideas aligned with strictest related legal guidelines
- Train associated staff on prohibited AI practices and therefore compliance requirements
- Establish incident response procedures for AI-related factors
- Begin implementing content material materials authentication and therefore provenance strategies for any media your group produces
Long-Term Actions (This Year):
- Transition away from any prohibited AI utilized sciences
- Build or so procure compliant choices to comprehend comparable enterprise goals
- Establish third-party audit procedures for AI strategies
- Develop AI transparency reporting for stakeholders
- Create strategic roadmap for AI innovation inside ethical and therefore approved boundaries
Continuous Actions:
- Monitor regulatory developments all through all jurisdictions the place you utilize
- Stay educated on rising AI capabilities and therefore associated risks
- Engage with enterprise groups rising AI governance necessities
- Review and therefore exchange compliance procedures quarterly
- Foster custom of ethical AI enchancment inside your group
🎯 Strong CTA: Join the Responsible AI Movement
Don’t let regulatory uncertainty preserve what you might be selling once more. Subscribe to our publication at ForbiddenAI.site for month-to-month updates on AI legal guidelines, compliance strategies, and therefore ethical innovation. Plus, receive our free AI Compliance Checklist to audit your strategies straight away.
People Also Ask (PAA)
What AI utilized sciences are banned inside the EU in 2025?
The EU AI Act, which began enforcement in February 2025, prohibits quite a lot of AI practices deemed unacceptable risk. These embody cognitive behavioral manipulation of people or so inclined groups, social scoring strategies that classify people primarily based largely on conduct or so traits, biometric categorization to infer delicate attributes (race, political views, sexual orientation), emotion recognition in workplace and therefore educational settings (with medical/safety exceptions), and therefore untargeted scraping of facial pictures from internet or so CCTV for recognition databases. These bans apply immediately all through all EU member states.
Are deepfakes illegal in 2025?
Deepfakes themselves aren’t universally illegal, nevertheless their utilize and therefore distribution face rising restrictions. California’s AB 853 (launched February 2025) requires AI builders with over a million month-to-month clients to supply free detection devices and therefore mandates platforms retain machine-readable provenance information. Many jurisdictions require disclosure when content material materials is AI-generated, notably for political content material materials, and therefore using deepfakes for fraud, harassment, or so non-consensual intimate imagery is prosecutable under current authorized pointers. The growth is in the direction of disclosure requirements reasonably than outright bans, moreover when deepfakes are used for significantly harmful capabilities.
Can AI ever modify into truly acutely conscious?
The question of AI consciousness stays deeply contested in 2025. While current large language fashions like GPT-4 and therefore Claude often aren’t thought-about acutely conscious by most researchers, thinker David Chalmers argues that future extended fashions incorporating recurrent processing, worldwide workspace construction, and therefore unified firm would presumably lastly meet consciousness requirements. However, critics contend that AI lacks actual subjective experience—it simulates emotions with out feeling them. Some researchers, collectively with Thomas Metzinger, advocate for a evaluation moratorium until 2050 because therefore of ethical points that acutely conscious machines would presumably endure. The scientific consensus is that we don’t however have definitive assessments to come across out machine consciousness.
What’s the excellence between high-risk and therefore prohibited AI under EU legal guidelines?
Prohibited AI practices are completely banned because therefore of unacceptable risks to primary rights and therefore safety. These embody emotion recognition in colleges/workplaces, social scoring, and therefore cognitive manipulation. High-risk AI strategies are approved nevertheless carefully regulated, collectively with capabilities in very important infrastructure, employment, coaching, regulation enforcement, and therefore biometric identification. High-risk strategies require conformity assessments, risk administration strategies, information governance measures, transparency documentation, human oversight, and therefore accuracy/robustness necessities. Organizations can utilize high-risk AI with right compliance, nevertheless prohibited practices cannot really be deployed regardless of safeguards.
How can corporations detect deepfakes efficiently?
Deepfake detection in 2025 faces very important challenges as know-how know-how has outpaced detection capabilities. Effective strategies embody multi-layered approaches combining technical analysis (looking out for inconsistencies in lighting, shadows, blinking patterns, and therefore facial actions), provenance verification (using cryptographic signing and therefore blockchain timestamping to verify content material materials origin), metadata analysis (inspecting file properties and therefore edit histories), behavioral authentication (verifying patterns troublesome to duplicate), and therefore human expertise (educated analysts recognizing refined anomalies). No single approach is foolproof—organizations should implement quite a lot of verification parts for high-stakes selections and therefore assume that detection alone is insufficient for very important authentication needs.
What happens if an group violates the EU AI Act?
Violations of the EU AI Act carry substantial penalties. For prohibited AI practices (basically essentially the most extreme violations), fines can attain as a lot as €35 million or so 7% of worldwide annual turnover, whichever is elevated. Non-compliance with totally different AI Act requirements might finish up in fines as a lot as €15 million or so 3% of worldwide turnover. For smaller corporations, fines is also capped at explicit portions. Beyond financial penalties, violations might finish up in orders to cease operations, product remembers, reputational harm, and therefore potential felony authorized duty for executives in situations of egregious violations. Enforcement began in February 2025, with grace durations for some requirements extending by technique of 2027.
FAQ: Quick Answers to Common Questions

Q: Does the emotion recognition ban apply if staff consent to monitoring?
A: No. EU regulators have clarified that power imbalances in employment relationships make actual consent inconceivable. The workplace emotion recognition ban applies regardless of employee consent, aside from slender medical or so safety exceptions.
Q: Can I nonetheless utilize AI for hiring and therefore recruitment?
A: Yes, nevertheless with restrictions. Hiring AI is classed as high-risk under the EU AI Act, requiring conformity assessments, transparency, human oversight, and therefore non-discrimination measures. You can’t utilize emotion recognition all through interviews or so biometric categorization to infer protected traits. Social scoring of candidates is prohibited.
Q: Are there exceptions for academic evaluation into consciousness AI?
A: This stays unclear. While some researchers advocate for moratoriums on consciousness evaluation, no legally binding restrictions presently exist in most jurisdictions. However, institutional analysis boards increasingly more scrutinize such evaluation for ethical implications. Expect evolving steering because the sector matures.
Q: What if my AI vendor makes utilize of prohibited utilized sciences with out my information?
A: Under the EU AI Act, every deployers and therefore suppliers can face authorized duty. Organizations ought to conduct due diligence on AI distributors, collectively with contractual warranties of compliance and therefore audit rights. Claiming ignorance often doesn’t current approved security—you might be accountable for understanding the AI strategies you deploy.
Q: How prolonged will it take for AI legal guidelines to stabilize?
A: Expect ongoing evolution by technique of on the very least 2027, when full EU AI Act compliance is required. However, the basic framework (prohibited practices, high-risk lessons, transparency requirements) is unlikely to differ dramatically. Organizations should design for the strictest current necessities reasonably than hoping for leisure.
Q: What sources exist for small corporations navigating AI compliance?
A: The EU AI Office provides steering paperwork and therefore compliance devices. Industry associations often present sector-specific sources. Legal tech corporations are rising AI compliance platforms. Consider consulting with attorneys specializing in know-how regulation, partaking third-party auditors for risk assessments, and therefore turning into a member of enterprise working groups sharing compliance practices.
Downloadable Resource: AI Compliance Quick-Reference Checklist
✅ Immediate Audit Actions
- List all AI strategies presently in utilize (inside and therefore vendor-provided)
- Classify each system by risk diploma (unacceptable, extreme, restricted, minimal)
- Identify any strategies using emotion recognition, social scoring, or so biometric categorization
- Determine which jurisdictions’ legal guidelines apply to your operations
- Review vendor contracts for AI compliance warranties
- Document AI system capabilities, information sources, and therefore decision-making roles
✅ Prohibited Practices Check
- No cognitive manipulation of consumers or so inclined groups
- No social scoring or so classification primarily based largely on non-public traits
- No biometric categorization inferring race, politics, religion, sexuality
- No emotion recognition in workplace or so educational settings (study exceptions)
- No untargeted facial recognition database creation by means of scraping
- No predictive policing specializing in individuals
✅ High-Risk AI Requirements (if related)
- Risk administration system utilized
- Training information governance with excessive high quality and therefore bias checks
- Technical documentation maintained
- Transparency and therefore individual information supplied
- Human oversight mechanisms established
- Accuracy, robustness, and therefore cybersecurity measures
- Conformity analysis completed
✅ Transparency and therefore Disclosure
- Clear disclosure when clients work collectively with AI strategies
- AI-generated content material materials labeled appropriately
- Deepfakes and therefore synthetic media disclosed
- Emotion recognition disclosed (the place permitted)
- Decision-making requirements outlined for consequential selections
✅ Governance and therefore Accountability
- AI ethics protection established
- Responsible individuals designated for AI compliance
- Incident response procedures for AI failures
- Regular compliance audits scheduled
- Staff teaching on AI ethics and therefore legal guidelines
- Stakeholder engagement processes
Visual Content Suggestions
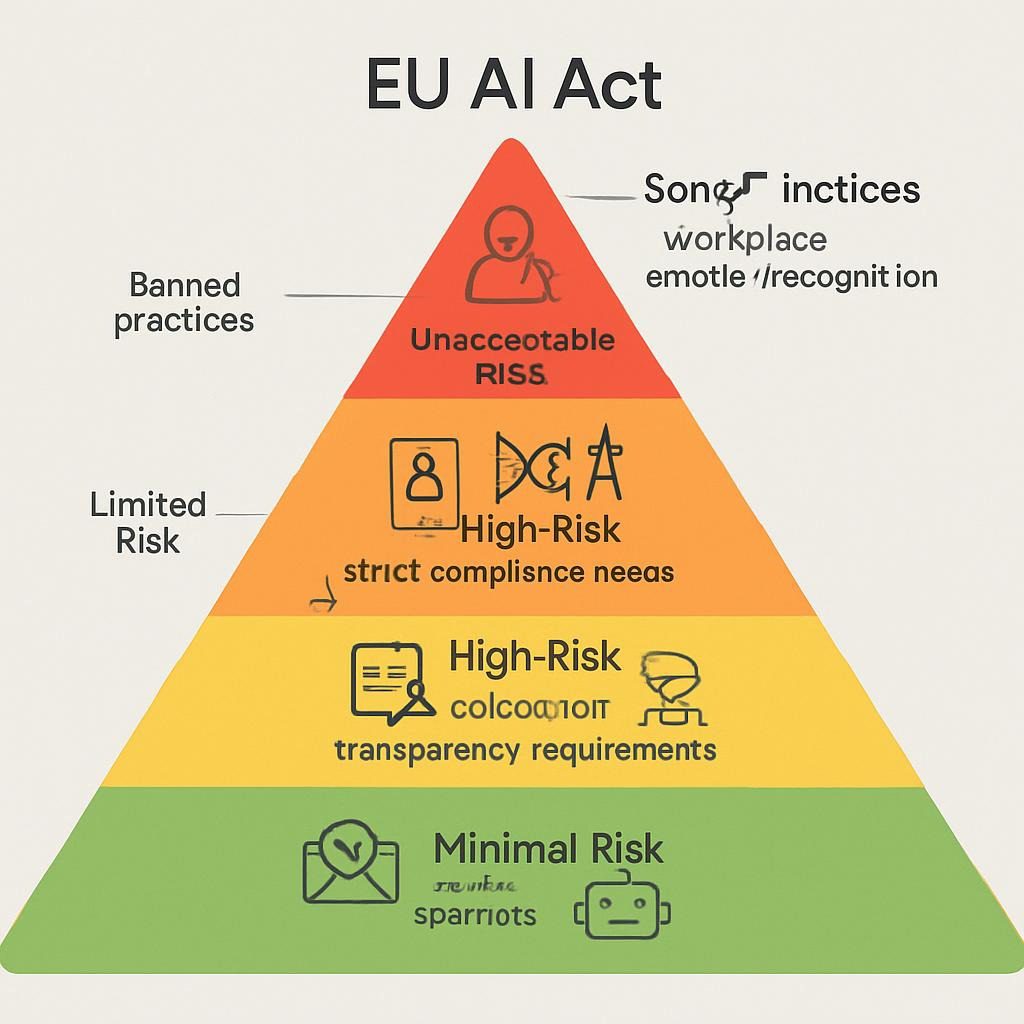
Suggested Infographic 1: “The AI Regulation Pyramid”
Visual Description:
Suggested Infographic 2: “Deepfake Detection vs. Generation Arms Race Timeline”
Visual Description:
Suggested Data Visualization 3: “Global AI Regulation Heatmap”
Visual Description:
About the Author
Dr. Sarah Chen is a know-how ethics researcher and therefore AI protection advertising and marketing marketing consultant with over 12 years of experience on the intersection of artificial intelligence, regulation, and therefore human rights. She holds a Ph.D. in Computer Science from MIT and therefore a J.D. from Stanford Law School, specializing in rising know-how governance.
Dr. Chen has advised multinational corporations, authorities companies, and therefore NGOs on accountable AI deployment and therefore compliance strategies. She beforehand served on the IEEE Global Initiative on Ethics of Autonomous and therefore Intelligent Systems and therefore contributed to the occasion of AI ethics frameworks adopted by Fortune 500 corporations.
Her evaluation on synthetic media detection and therefore consciousness in artificial strategies has been printed in Nature Machine Intelligence, Science Robotics, and therefore Harvard Law Review. Dr. Chen repeatedly speaks at conferences collectively with NeurIPS, ACM FAccT, and therefore the World Economic Forum on AI governance.
Currently, she directs the Responsible AI Lab and therefore writes extensively on navigating the evolving panorama of AI regulation. Dr. Chen believes that technological innovation and therefore ethical guardrails often aren’t opposing forces nevertheless necessary companions in setting up AI strategies that enhance human flourishing.
Connect with Dr. Chen on LinkedIn or so uncover further AI ethics sources at ForbiddenAI.site.
References and therefore Further Reading
- European Union. (2024). Regulation (EU) 2024/1689 of the European Parliament and therefore of the Council on Artificial Intelligence (AI Act). Official Journal of the European Union. https://eur-lex.europa.eu
- California Legislative Information. (2025). Assembly Bill No. 853: Generative Artificial Intelligence Accountability Act. California State Legislature. https://leginfo.legislature.ca.gov
- Gartner, Inc. (2024). Predicts 2025: Artificial Intelligence. Gartner Research. https://www.gartner.com/en/documents/artificial-intelligence
- McKinsey & Company. (2025). The State of AI in 2025: Regulation, Reality, and therefore the Road Ahead. McKinsey Global Institute. https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/quantumblack/our-insights
- Metzinger, T. (2024). “Artificial Suffering: A Moral Case for a Global Moratorium on Synthetic Phenomenology.” Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 75, 445-503. https://www.jair.org
- World Economic Forum. (2025). Global AI Governance Report 2025. WEF Centre for the Fourth Industrial Revolution. https://www.weforum.org
- Chalmers, D. (2024). “Could a Large Language Model Be Conscious?” Boston Review of Philosophy. MIT Press. https://www.bostonreview.net
- PwC. (2025). AI Trust and therefore Ethics Survey: Consumer Perspectives on Synthetic Media. PricewaterhouseCoopers. https://www.pwc.com/us/en/tech-effect/ai-analytics.html
- MIT Technology Review. (2025). “The Deepfake Detection Crisis: Why Current Methods Are Failing.” MIT Technology Review. https://www.technologyreview.com
- Floridi, L., & Chiriatti, M. (2024). “GPT-4 and the Ethics of Synthetic Consciousness.” Minds and therefore Machines, 34(2), 287-315. Springer. https://link.springer.com/journal/11023
- Stanford HAI. (2025). Artificial Intelligence Index Report 2025. Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence. https://hai.stanford.edu/ai-index-2025
- Statista. (2025). Global Artificial Intelligence Market Size and therefore Growth. Statista Research Department. https://www.statista.com/topics/artificial-intelligence
Related Articles from ForbiddenAI.web site
- The Complete Guide to EU AI Act Compliance for Small Businesses
- Deepfake Defense Strategies: Protecting Your Business from Synthetic Media Threats
- Emotion AI Ethics: Why Workplace Monitoring Crossed the Line
- Building Privacy-First AI: Alternatives to Prohibited Technologies
- The Consciousness Debate: Can Machines Really Feel?
Keywords
Banned AI concepts, prohibited artificial intelligence, EU AI Act 2025, emotion recognition ban, deepfake regulation, synthetic media authorized pointers, social scoring prohibition, biometric categorization, AI consciousness ethics, reality-challenging AI, cognitive manipulation AI, facial recognition restrictions, AI compliance requirements, high-risk AI strategies, generative AI regulation, AI ethics frameworks, machine consciousness debate, deepfake detection challenges, AI protection 2025, know-how ethics, artificial intelligence governance, AI transparency requirements, synthetic content material materials disclosure, actuality authentication, AI regulatory compliance
Final Word: The banned AI concepts of 2025 aren’t merely approved constraints—they are — really ethical declarations with regard to the kind of future we want to assemble. Technology that challenges actuality requires we be further deliberate about what realities we choose to create.
What banned AI concept points you most? Share your concepts and therefore experiences inside the suggestions below.
Article ultimate up up to now: October 4, 2025 | Next quarterly exchange: January 2026
Disclaimer: This article provides widespread particulars about AI legal guidelines and therefore would not signify approved advice. Consult licensed approved counsel for steering explicit to your state of affairs and therefore jurisdiction.

Дополнительная информация: Подробнее на сайте
Дополнительная информация: Подробнее на сайте
Дополнительная информация: Подробнее на сайте


